Natural language understanding (NLU) is a branch of artificial intelligence (AI) that uses computer software to understand input in the form of sentences using text or speech. NLU enables human-computer interaction by analyzing language versus just words.
NLU enables computers to understand the sentiments expressed in a natural language used by humans, such as English, French or Mandarin, without the formalized syntax of computer languages. NLU also enables computers to communicate back to humans in their own languages.
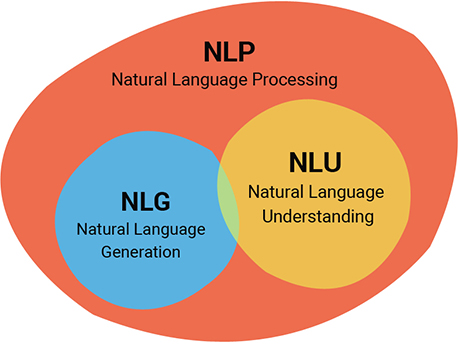
Natural-Language Understanding (NLU) or Natural-Language Interpretation (NLI) is a subset of natural-language processing in artificial intelligence that deals with machine reading comprehension.
How does natural language understanding work?
NLU analyzes data to determine its meaning by using algorithms to reduce human speech into a structured ontology - a data model consisting of semantics and pragmatics definitions. Two fundamental concepts of NLU are intent and entity recognition:
- Intent recognition is the process of identifying the user's sentiment in input text and determining their objective. It's the first and most important part of NLU, as it establishes the meaning of the text.
- Entity recognition is a specific type of NLU that focuses on identifying the entities in a message and then extracting the most important information about those entities. There are two types of entities: named entities and numeric entities. Named entities are grouped into categories, such as people's names, business names and locations. Numeric entities are recognized as quantities, dates, currencies and percentages.
Why is natural language understanding important?
Human language is typically difficult for computers to grasp, as it's filled with complex, subtle and ever-changing meanings. Natural language understanding systems let organizations create products or tools that can both understand words and interpret their meaning.
NLU makes it possible to carry out a dialogue with a computer using a human-based language. This is useful for consumer products or device features, such as voice assistants and speech to text.



By using NLU, conversational interfaces can understand and respond to human language by segmenting words and sentences, recognizing grammar and using semantic knowledge to infer intent.